H5n1 who – Unveiling the enigmatic H5N1 virus, this article delves into its nature, impact on humans and poultry, surveillance methods, prevention strategies, and pandemic preparedness measures, providing a comprehensive understanding of this global health concern.
From its transmission routes to its potential severity, we explore the complexities of H5N1 in humans, examining its prevalence, risk factors, clinical manifestations, and mortality rates.
H5N1 Virus: General Overview
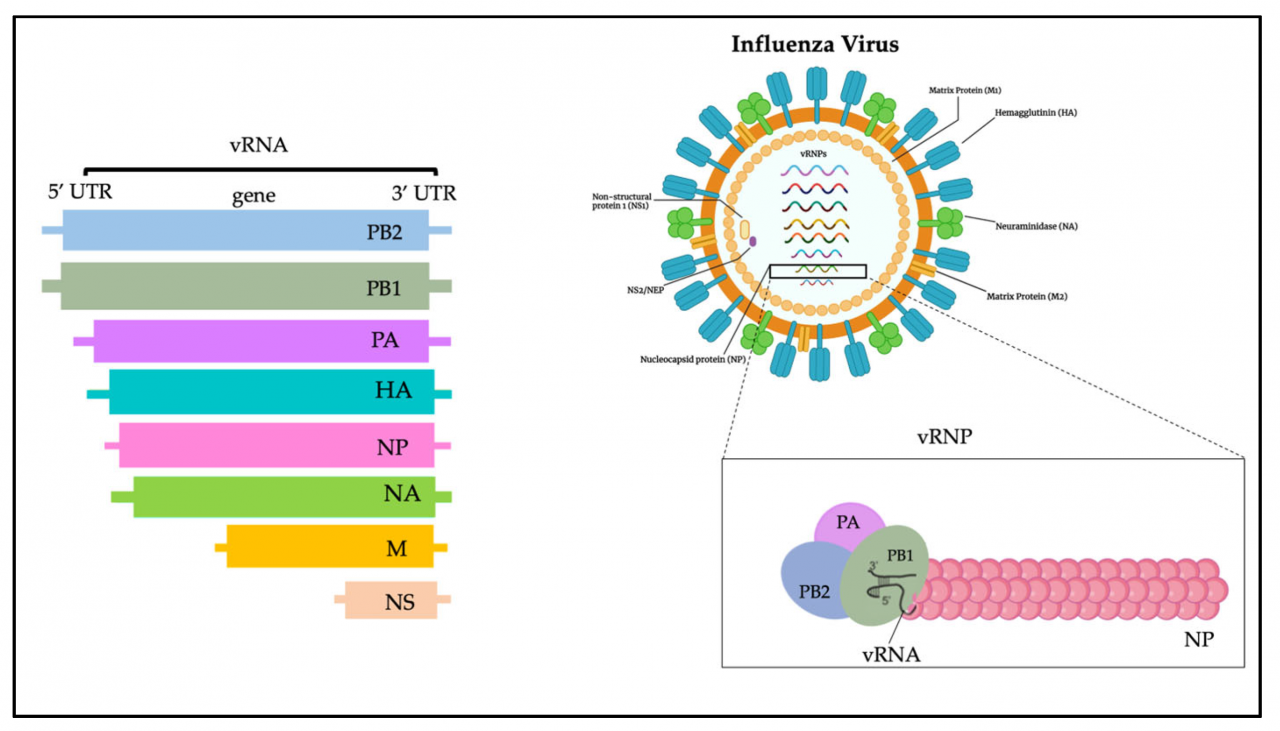
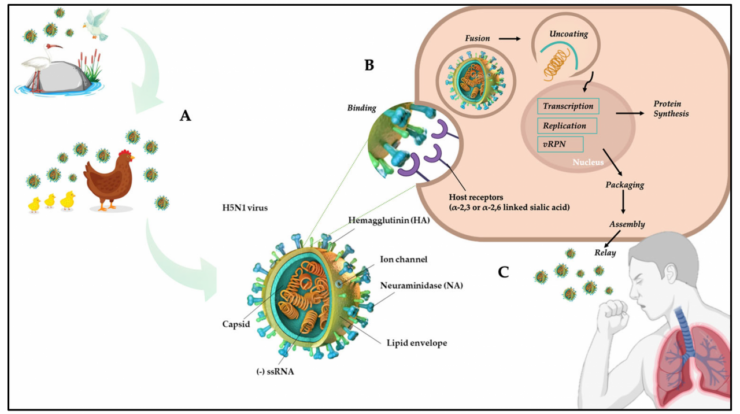
The H5N1 virus is a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that can cause severe illness and death in both poultry and humans. It is a type A influenza virus, belonging to the Orthomyxoviridae family.
The H5N1 virus is primarily transmitted through contact with infected birds or their secretions, such as saliva, feces, or respiratory droplets. It can also be transmitted through contaminated surfaces or objects. In humans, the virus typically causes respiratory symptoms, ranging from mild flu-like illness to severe pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Transmission Methods
- Contact with infected birds or their secretions
- Inhalation of contaminated respiratory droplets
- Contact with contaminated surfaces or objects
Symptoms in Humans
- Fever
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Muscle aches
- Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty breathing
Potential Severity
H5N1 can cause severe illness and death in both poultry and humans. The mortality rate in humans is estimated to be around 60%, making it one of the most deadly influenza viruses known.
H5N1 in Humans: Epidemiology and Impact
Human H5N1 infections have been reported in over 60 countries worldwide, with the majority of cases occurring in Asia. The virus has caused significant morbidity and mortality, particularly in Southeast Asia.
The geographic distribution of human H5N1 cases is closely linked to poultry farming practices and the prevalence of the virus in poultry populations. Risk factors for human infection include close contact with infected poultry, working in the poultry industry, and living in areas with high levels of poultry farming.
Clinical Manifestations
The clinical manifestations of H5N1 infection in humans can vary widely, ranging from mild flu-like symptoms to severe pneumonia and ARDS.
Severity and Mortality Rates
The severity and mortality rates of H5N1 infection in humans are significantly higher than those of seasonal influenza viruses. The overall case fatality rate is estimated to be around 60%, although it can vary depending on the strain of the virus and the patient’s health status.
H5N1 in Poultry: Implications and Control Measures
H5N1 has had a devastating impact on poultry populations worldwide, leading to significant economic losses and disruptions to the poultry industry.
The virus can spread rapidly through poultry flocks, causing high mortality rates. Infected birds may show respiratory symptoms, such as coughing, sneezing, and difficulty breathing, as well as decreased appetite and egg production.
Economic Consequences
H5N1 outbreaks can have a significant economic impact on the poultry industry, leading to losses in productivity, trade restrictions, and consumer concerns.
Control Measures
Control measures for H5N1 in poultry include:
- Biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of the virus into poultry flocks
- Vaccination of poultry
- Surveillance and monitoring for early detection and containment of outbreaks
- Culling of infected flocks
H5N1 Surveillance and Monitoring
Surveillance and monitoring are essential for tracking H5N1 activity and preventing its spread.
Surveillance involves the collection and analysis of data on H5N1 infections in both poultry and humans. This data is used to identify areas of high risk, monitor the evolution of the virus, and evaluate the effectiveness of control measures.
Methods, H5n1 who
Surveillance methods for H5N1 include:
- Laboratory testing of samples from poultry and humans
- Monitoring of poultry flocks for signs of infection
- Collection of epidemiological data on human cases
International Collaboration
International collaboration is essential for effective H5N1 surveillance and monitoring. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) coordinate global efforts to track the virus and share information.
H5N1 Prevention and Treatment
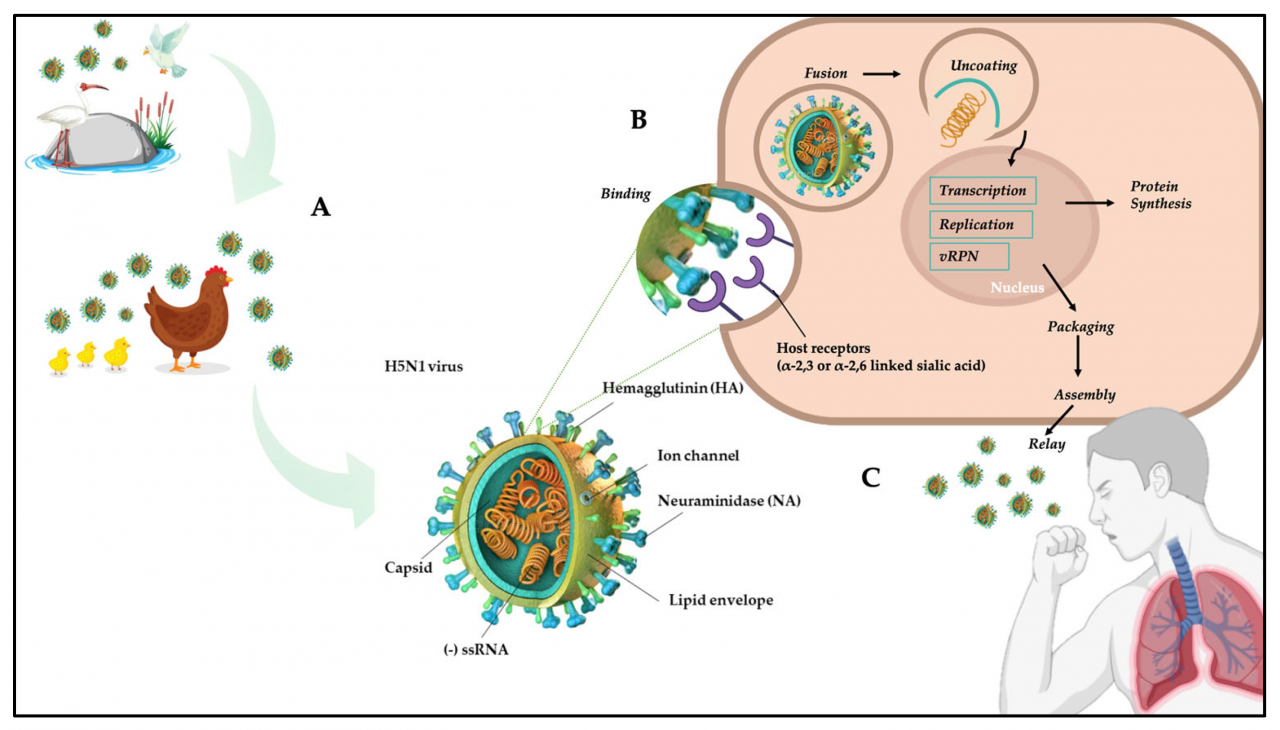
Prevention and treatment of H5N1 are critical to reducing the risk of infection and mitigating its impact.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures for H5N1 include:
- Avoiding contact with infected birds or their secretions
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding touching the face
- Getting vaccinated against H5N1 (if available)
Treatment
Treatment for H5N1 infection typically involves antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza).
H5N1 Pandemic Preparedness and Response: H5n1 Who
A potential H5N1 pandemic is a major concern due to the virus’s high mortality rate and its ability to spread rapidly.
Pandemic preparedness and response measures include:
- Developing and stockpiling vaccines and antiviral medications
- Strengthening surveillance and monitoring systems
- Developing plans for containment and mitigation of outbreaks
- Educating the public about H5N1 and preventive measures
International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for effective pandemic preparedness and response. The WHO coordinates global efforts to monitor the virus, share information, and develop coordinated strategies.
Conclusion
As the world remains vigilant against the threat of H5N1, ongoing research and international collaboration are crucial for developing effective vaccines, treatments, and surveillance systems. Understanding the virus’s behavior and implementing proactive measures are essential to mitigate its impact and safeguard public health.